NEET Biology Notes Animal Kingdom Cockroach
Cockroach
Cockroach
- Two species of cockroaches commonly found in India are Periplaneta americana and Blatta orientalis. Periplaneta americana is the largest and most common species. The generic name Periplaneta was given by Burmeister in 1838. Cockroaches are nocturnal and cursorial. Body is divided into head, thorax and abdomen. Head is derived by the fusion of six embryonic segment. Exoskeleton of each segment consists of four chitinous plates called sclerites.
- Mouth parts of cockroaches are mandibulate type or cutting and chewing type. Anal styles, a pair of small, spine-like unjointed structures are present on sternite of 9th segment in males only. The body cavity of cockroach is a haemocoel filled with blood. Circulatory system of cockroach is open type. Heart of cockroach is neurogenic and longitudinally beaded with 13 chambers. Excretory organs of cockroach are Malpighian tubules.
- Prothoracic gland secrete a moulting hormone called ecdysone. Corpora allata is neurosecretory and secretes, juvenile hormone. Respiratory system of cockroach consists of tracheal system. Each compound eye of cockroach is composed of about 2000 visual/units called ommatidia.
- Apposition image is formed in cockroach. In cockroach, sexes are separate, so dioecious or unisexual animal. Testes of cockroach are located in the abdominal segments 4, 5 and 6. They produce sperms. Male organs consist of testes, vasa deferentia, ejaculatory duct, mushroom gland, phallic or conglobate gland and male gonapophysis. Female organs consist of ovaries, oviduct, vagina, genital chamber, spermathecae, colleterial glands and female gonapophysis Ovaries of cockroach are located in abdominal segments 2-6. Each ovary is made up of eight ovarioles.
Phylum-Mollusca
It has free-living aquatic forms (freshwater or marine), some are amphibious. Body is soft and unsegmented, enclosed in a glandular mantle usually covered by a shell. Coelom is reduced to a cavity around the heart. The study of molluscs is called ‘malacology’. „
Digestive system is complete. Respiratory organs are in the form of gills called ctenidia. Locomotory structure is represented by muscular foot. They have soft-body, which is differentiated into three regions, i.e. head, visceral hump and foot. Visceral hump is covered by a thin, fleshy mantle. Mantle secretes a calcareous shell, which may be external or internal. Reproduction is sexual. Either unisexual or bisexual, development is direct, e.g. Pila (snail), Sepia, Unio (freshwater mussel), Octopus and Chiton.
Pila
Pila (apple snail) is an amphibious mollusc found in ponds, rice, field, etc. It shows creeping locomotion; herbivorous in nutrition; aestivates during summer; respires with gill in water and pulmonary sac on land. Sexes show sexual-dimorphism (male has large sized penis). Fertilisation is internal. Female is oviparous and development is direct.
These are as follows :
- Body is covered by a univalvular, unilocular and spirally-coiled shell.
- Lowermost whole, called body whorl, is largest and is opened by lunate-shaped mouth, which can be closed by an operculum during defence.
- Shell has vertical lines of growth.
Sepia
- Sepia (cuttle fish) is a marine mollusc, a good swimmer and carnivorous in nutrition (feed on fishes, crustaceans, etc.). It defends by protective colouration, a smoke-screen of Sepia ink and backward darting (with its siphon). Sexes show sexual-dimorphism (male with hectocotylised arm). Fertilisation is internal, development is direct. Body is differentiated into two parts, i.e. head and trunk.
- Head has one pair of eyes, 8 sucker-bearing arms and 2 long tentacles surrounding the mouth.
- Trunk bears one pair of lateral fins for swimming. On the ventral side on junction of head and trunk, it has a funnel or siphon for backward darting.
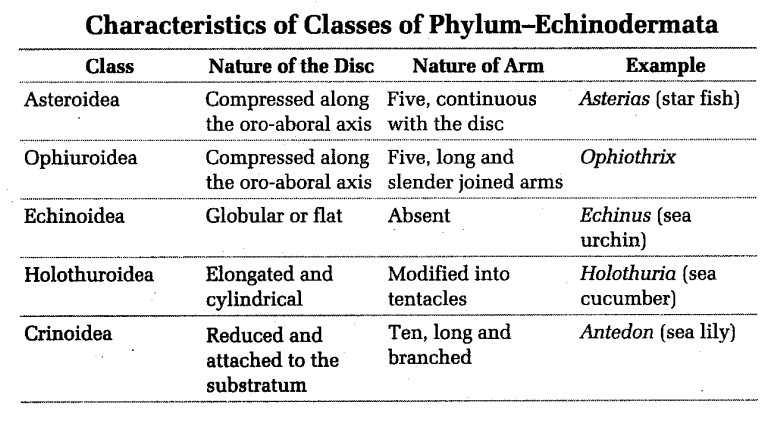
Phylum-Echinodermata
It has free-living, exclusively marine forms. Adults are radially symmetrical, while larvae are bilaterally symmetrical. Body is represented by a central disc covered by ossicles with spines called pedicellariae. Disc may bear extensions called arms. Digestive system is complete. A unique ambulacral or water vascular system is present.
Tube feet are present for locomotion and respiration. These are extended and retracted by variation in hydraulic pressure of the fluid in them and contraction of their muscles. Nervous system has a central nerve ring with five radiating nerves. Reproduction is sexual. Sexes are separate. Development is indirect. It show very high power of regeneration. Tube feet are used for feeding as well, for locomotion, e.g. Asterias, Ophiothrix, Echinus, Antedon, Holothuria, etc.
Asterias (Star Fish)
Mouth is present on the oral surface, five narrow ambulacral grooves are also found, bright red eye lies at the terminal end of each ambulacral grooves. The aboral surface bears many stout spines distributed irregularly.
Soft dermal branchiae are present between the spines. They act as respiratory and excretory organs. In between two arms, near the anus, a perforated circular plate, is present called the madreporite. There are microscopic pincer-like structures known as pedicellariae, which also act as organs of offence. Pedicellariae also remove foreign substances and keep the body surface clean.
Echinus
Echinus (sea urchin) is an omnivorous, found in rocky sea bottom. It uses teeth for feeding and moves with the help of spines. Pedicellariae are present among the spines. The mouth is present in the centre of oral surface.
The sea urchin has a masticatory apparatus, called Aristotle’s Lantern, which formed by five strong and sharp teeth. It projects slightly through the mouth. The anus is a smaller aperture.
Phylum-Chordata
This phylum is characterised by three unique features, at least during the early stages of their development. Only in Amphioxus all three chordate characters present through out life. Auricularia is connecting link between Chordata and non-chordata.
A rod-like structure called notochord lying above the digestive tract. A tubular dorsal nerve cord lying above the notochord. A pair of gill slits in the pharyngeal region. Only the nerve cord persists throughout the life of the organism.
The notochord is usually replaced by a vertebral column in vertebrates and the gill slits disappear during the embryonic stage. The phylum is divided into four sub-phyla Hemichordata, Urochordata, Cephalochordata (together called asprotochordates) and Veru orata.

Sub-phylum-Urochordata
Marine in habitat, notochord is found in the tail in larval form. Hollow nerve cord is also present in the larva. Body is covered by a tunic. Pharynx hac several gill slits.
e.g. Herdmania, Doliolum and Pyrosoma.
Sub-phylum-Cephalochordata
Headless, tiny fish-like chor dates. Notochord, nerve cord without a distinct brain, gill slits and a post-anal tail present.
e.g. Branchiostoma (Amphioxus).
Sub-ph vltim-Vertebra la –
This includes the majority of chordates. Head is prominent. Nervous system and exoskeleton are highly developed. Notochord is replaced by a jointed vertebral column. Two pairs of appendages (limbs).
Mammals exhibit the following unique features:
- The presence of mammary glands to nourish the young ones.
- The presence of muscular diaphragm that separates thorax from abdomen.
- The presence of external ear called pinna.
- The presence of seven vertebrae in the neck region, e.g. phylum-Chordata


Scoliodon
Scoliodon dumerili (dogfish) is seen in the Bay of Bengal. It is carnivorous normally found as feeding upon Indian shark, other fishes, crabs, etc. The male can be distinguished from the female, with the help of a pair of hard elongated claspers attached to the pelvic fins. These are copulatory organs. Scoliodon is eaten as food by some people. Liver oik is also extracted from it, which is rich in vitamin-A and D. Fish meat is used as fertiliser and poultry feed. Shark skin provides leather and their pituitary extract is used for medical purposes.
Torpedo
Torpedo (electric ray) is a bottom-living marine fish, famous for discharging electricity, which is sufficient enough to stun preys such as small fishes, etc., It is a carnivorous fish with smooth skin (without scales). The spiracles are situated behind the eyes and are used for taking in water for gaseous exchange. Both the pectoral fins are fused with the trunk and a pair of electric organs are situated on the dorsal side of the trunk region.
Ram tigrina
Rana tigrina (common Indian frog) is an amphibian found in and near freshwater bodies. It is diurnal, carnivorous in nature. It hibernates in winter and aestivates in summer. It also defends itself by metachrosis (protective colouration).
Sexes show sexual dimorphism. Male has vocal sacs (to croak to call the female) and amplexary pads (to grip the female during copulation). Female is oviparous. Fertilisation is external. Eggs are laid in an irregular gelatinous mass called spawn. Development includes an aquatic tadpqle larva, which undergoes metamorphosis.
Head bears mouth, nostrils, large bulging eyes on dorso-lateral sides and eardrum just behind and below eye. Trunk bears two pairs of pentadactyl limbs. Hind limbs are much longer for leaping. Webs are present between the toes only. Each forelimb has four fingers (pollex absent). On the ventral side of index (first finger), there is amplexary or nuptial pad. Trunk also has longitudinal wrinkles of skin,« called dermal plicae on dorsal side and a cloacal aperture at the posterior end.
Bufo melanostictus
Bufo melanostictus (Indian toad) is a terrestrial amphibian nocturnal in activity, carnivorous in diet and hibernating in winter. It defends itself by secreting an irritating fluid from skin (poison) glands.
Sexes are separate. Female is oviparous and lays eggs spawn (in which eggs are laid in water in chains). Fertilisation is external. Development includes a tadpole larva.
Toad is similar to frog in basic morphological characters except that
- Skin is dry, rough, warty and non-glandular.
- The presence of parotid glands behind eardrums.
- Webs absent frpm between the toes.
- Horny tip of the digits.
Testudo
Testudo (tortoise) is a semi-terrestrial reptile, diurnal in activity, omnivorous (feed on vegetation as well as insects, worms, etc.) in diet, hibernates in winter. Sexes show sexual dimorphism.
Male has copulatory organ penis. Female is oviparous and development is indirect. When disturbed, it can withdraw its head, neck, limbs and tail into a bony tortoise shell. Body is covered by a tortoise shell. Body is divided into four parts, i.e. head, neck, trunk and tail. All body parts can be hidden within tortoise shell during defence. Trunk bears two pairs of pentadactyl limbs. Each digit ends into a claw.
Naja naja
Naja naja (cobra) is a poisonous snake. Its venom is neurotoxic. Its venom is used in cancer research studies. It is a terrestrial snake generally found in thick vegetation, under stones, infested house, etc. It is diurnal in activity; carnivorous and show cannibalism, hibernates in winter, raises the head and expands its neck as hood and hisses loudly in self-defence through the nostrils.
Sexes are unisexual, fertilisation is internal and female is oviparous. Body is long and cylindrical; blackish or brown coloured. Body is divisible into four parts, i.e. head, neck, trunk and tail. Head bears terminal and wide mouth, eyes, nostrils, but no tympanum. It is covered by large sized head shields (scales). Ocular shield is transparent and covers eye.
Neck has two eye spots on the dorsal side (called binocellate cobra) and can be expanded as a hood. Trunk is limbless.
Struthio
Stmthio (ostrich) is the largest (240 cm high) terrestrial bird found in desert of Africa and Arabia. It is diurnal and gregarious in activity, omnivorous in diet and cursorial (with long legs having pads under the toes) in locomotion. Sexes are unisexual and male is polygamous. It is larger than female and also has a penis. Fertilisation is internal and female is oviparous (largest sized egg). Male incubates the eggs.
Body is divided into four parts, i.e. head, neck, trunk and tail. Head is small sized and bears eyes, nostrils and mouth bounded by beak.
Neck is long and naked. Forelimbs (wings) are vestigial, while hindlimbs are very larged sized. Each foot has only two toes with pads on their undersurface. Tail is reduced.
Columba livia
Columba livia (pigeon) is a cosmopolitan and terrestrial bird very commonly seen in grain markets, warehouses, etc. It is diurnal and gregarious in activity omnivorous (mainly feed on grains but sometimes even on insects) in diet, slow-walking and rapid flying type locomotion.
Sexes do not show sexual dimorphism. Male is monogamous. Fertilisation is internal and females are oviparous. Both sexes incubate the eggs.
Balaenoptera indica
Balaenoptera indica (whale) is a gregarious marine mammal of large size, which feeds on small fishes, molluscs, crustaceans, etc., including plankton. Whale swims with the help of tail and flippers. It can remain submerged for several minutes.
Echolocation sends out a thick cloud of air mixed with water drops to several metres in height. The upper jaw bears a whale bone, consisting of two rows of 600-800 plates. Its bone acts as a strainer. It is hunted for its blubber.
Platanista gangetica
Platanista gangetica (dolphin) is a highly intelligent aquatic mammal, which can imitate human laughter. It moves in shoals and feeds on arthropods, molluscs and fishes.
The body is 2-3 metres long with beak like rostrum having numerous teeth. Pinna is absent. Forelimbs are modified into flippers. Hindlimbs are absent. River dolphin (Vernsus) of India is found in Gangas and Brahmputra. It is also found in Pakistan, China and Latin Americas.