Contents
The study of human anatomy and physiology is a crucial branch of Biology Topics.
Types of Plants – Definition, Examples and Diagrams
A neem tree, Bougainvillea and grass, are all plants. There are a large number of plants around us. A garden has many plants of various shapes and sizes. The grass in the lawn are also plants. And if we go to village side, we can see the crop plants grown in the fields all around. At our home and school also we have a large number of plants, including potted plants (Plants grown in pots are called potted plants).
Though plants are living things (or living organisms), they grow in the soil and remain fixed at a place through their roots. Plants do not move around like animals do. Plants also do not take food like animals. The plants make their own food by the process of photosynthesis. Plants are of different shapes and sizes. Some plants are very big, some are medium-sized, some are small whereas some are just patches of green material on the soil. Most of the plants have green leaves. A few plants have reddish leaves.
Most of the plants bear flowers. They are called flowering plants. Some of the examples of flowering plants are : Rose, Mango, Neem, Bougainvillea, Mustard, Sunflower plant, Grass, Lemon, Wheat, Maize, Chilli, Tomato, Tulsi, Peepal, Banyan, Banana, Sugarcane and Potato. Some of the plants, however, do not bear flowers. They are called non-flowering plants (or flowerless plants). Some of the examples of non flowering plants are : Ferns, Moss, Algae, Fungi (like Mushroom), and Conifers (like Pine trees).
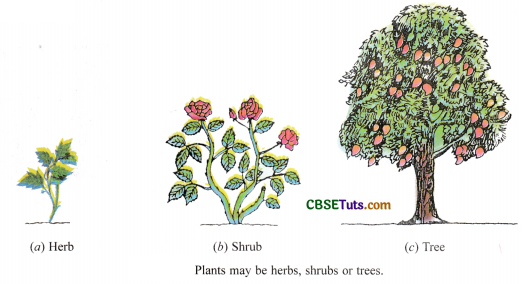
Most of the plants can be classified into three main groups : herbs, shrubs and trees, on the basis of their size, nature of stem and life-span. So, plants may be herbs, shrubs or trees. We will now discuss all these types of plants, one by one. Let us start with herbs.
1. Herbs
Herbs are small plants having a soft and delicate stem. Herbs do not have woody stem. They are non-woody plants. Herbs have a green and tender stem. We can easily bend the stem of a herb. A herb is shown in Figure (a). Herbs are short-sized plants. Herbs usually do not grow more than one metre in height. Herbs have a short life-span. They may live for only one or two seasons. Some of the examples of herbs are : Tomato, Mustard, Radish, Sunflower, Wheat, Paddy (Rice), Cabbage, Carrot, Ginger and Turnip. Please note that though the stems of herbs are soft and delicate but they are strong enough to stand erect on their own.
2. Shrubs
Shrubs are medium-sized plants with a hard and woody stem, branching out near the base. Though the stem of a shrub is hard but it is not very thick. Actually, shrubs do not have a distinct main stem or trunk. Shrubs tend to branch near ground level, so many branches are seen rising just above the ground (giving them a bushy appearance). A shrub is shown in Figure (b). Some of the examples of shrubs are: Rose, Jasmine (Chameli), Croton, Tulsi, Bougainvillea, China rose (Shoe flower), Pomegranate, Henna (Mehndi), and Lemon. The shrubs are bigger than herbs but smaller than trees. The life-span of shrubs is for many years but it is less than that of trees.
3. Trees
Trees are tall and big plants with hard and thick woody stem. The trees have one main stem called ‘trunk’ which usually gives out branches and leaves. The branches in a tree appear higher up on the stem (much above the ground). A tree is shown in Figure 1(c). Some of the examples of trees are : Neem, Mango, Palm, Teak, Oak, Sandalwood, Coconut, Eucalyptus, Banyan (Bargad) and Jamun. Please note that palm trees are never branched. The coconut tree is a type of palm tree. The trees are very big in size. The life-span of trees is very large. Trees usually live for many, many years.
Shrubs and trees are both woody plants. The main differences between shrubs and trees are the following :
- Shrubs are medium-sized plants whereas trees are very tall and big plants.
- Shrubs branch near the ground whereas trees branch much above the ground.
- Shrubs have thin stem whereas trees have thick stem.
There are some plants which are different from herbs, shrubs and trees. These are called ‘climbers’ and ‘creepers’. Climbers and creepers are the plants with very weak stems which cannot stand upright (or erect) on their own. We will now discuss climber and creeper plants in somewhat detail.
Climbers
A plant having thin, long and weak stem which cannot stand upright but readily climbs up a neighbouring support (like a fence) or a tree is called a climber (or climber plant). A climber plant has special organs for climbing called ‘tendrils’ (some climber plants have stem tendrils whereas others have leaf tendrils). The tendrils of climber plants wind themselves around any neighbouring object and help the plant to climb up. In Figure, the stem tendril of a climber plant is winding around a bamboo stick for supporting the plant. Some of the examples of climbers (or climber plants) are : Pea plant; Bitter gourd (Karela); Sweet gourd (Mitha kaddu); Bottle gourd (Lauki); Grape vine ; Passion flower and Glory lily. All these plants have various types of tendrils in them.

Creepers
A plant having thin, long and weak stem which cannot stand upright and spreads on the ground, is called a creeper (or creeper plant). A creeper plant has no climbing organs like tendrils (which are present in climber plants). A creeper grows along the ground or other surfaces by extending long shoots (or branches). The two important creepers (or creeper plants) are: Strawberry plant and Money plant (see Figure). If a creeper plant is to be grown like a climber plant, then the top end of its stem has to be tied with a string and the other end of string fixed at a height. For example, a money plant can be made to grow up by tying a string to its top end. Please note that the main difference between the climber plants and creeper plants is that climber plants have climbing organs like tendrils (on their stems or leaves) but creeper plants have no such climbing organs. We will now answer one question based on the classification of plants.
Example Problem.
Classify the following as herbs, shrubs and trees :
Jasmine, Rose, Palm, Mustard, Radish, Neem, Mango, Sunflower, Tulsi.
Answer:
Herbs
Mustard
Radish
Sunflower
Shrubs
Jasmine
Rose
Tulsi
Trees
Palm
Neem
Mango