NEET Physics Chapter Wise Mock Test – Thermodynamics
Question 1:
1 cc of water at its boiling point (100°C) absorbs 540 cal of heat to become steam with a volume of 1671 cc. If the atmospheric pressure is 1.013 x105 Nm-2, the energy spent (in cal) to overcome molecular attractive forces is nearly (mechanical equivalent of heat = 4.2 J/cal)
(a) 540
(b) 500
(c) 40
(d) zero
Question 2:

Question 3:
A bread gives a boy 5000 cal. How much height he can climb by using this energy, if his efficiency is 28%? (Mass of the boy = 60 kg)
(a) 2.5 m
(b) 5 m
(c) 10 m
(d) 15 m
Question 4:
A person of mass 60 kg wants to lose 5 kg by going up and down a 10 m high stairs. Assume he burns twice as much fat while going up than coming down. If 1 kg of fat is burnt on expanding 7000 kilo calories, how many times must be go up and down to reduce his weight by 5 kg?
(a) 10.5 x 103
(b) 24.3 x 103
(c) 16.3 x 103
(d) 9×103
Question 5:
When one mole of monoatomic gas expands at constant pressure, the ratio of the heat supplied that increases the internal energy of the gas and that is used in expansion is
(a) ∞
(b) zero
(c) 3/2
(d) 2/3
Question 6:
In a thermodynamic process with 2 moles of gas, 30 J of heat is released and 22 J of work is done on the gas. Given that initial internal energy of the sample was 20 J,what will be the final internal energy?
(a) 72 J
(b) 32 J
(c) 28J
(d) 12 J
Question 7:
Which of the following processes is reversible?
(a) Transfer of heat by radiation
(b) Electrical heating of a nichrome wire
(c) Transfer of heat by conduction
(d) Isothermal compression
Question 8:
One mole of oxygen is expanded from a volume 1 L to 5 L at a constant temperature T = 280 K. The change in internal energy is
(a) 0.22 kJ
(b) 22 J
(c) 0.11 kJ
(d) 11 J
Question 9:
A sample of perfect gas is compressed isothermally to half its volume. If it is compressed adiabatically to the same volume, the final pressure of the gas will be
(a) more
(b) less
(c) same
(d) more or less depending on the initial temperature of the gas
Question 10:
Which of the fallowing statements is true about the indicator diagram of adiabatic and isothermal processes?
(a) The slope of isothermal is more than that of adiabatic
(b) The slope of adiabatic is more than that of isothermal
(c) Both are parallel straight lines
(d) Both are parallel curves
Question 11:
An ideal gas at 27°C is compressed adiabatically to 8/27 of its original volume. The rise in temperature is (take, γ = 5/3)
(a) 475°C
(b) 150°C
(c) 275°C
(d) 402°C
Question 12:
A monoatomic gas (γ = 5/3) at pressure p is suddenly compressed to 1/64th of its volume adiabatically. Then, pressure of gas is
(a) 8 p
(b) 42/3 p
(c) 256 p
(d) 1024p
Question 13:
A gas is compressed adiabatically till its temperature is doubled. The ratio of its final volume to initial volume will be
(a) 1/2
(b) more than 1/2
(c) less than 1/2
(d) between 1 and 2
Question 14:
One mole of an ideal gas at an initial temperature of T K does 6 R J of work adiabatically. If the ratio of specific heats of this gas at constant pressure’and at constant volume is 5/3, the final temperature of gas will be
(a) (T + 2.4) K
(b) (T – 2.4) K
(c) (T + 4) K
(d) (T – 4) K
Question 15:
A gas is compressed at a constant pressure of 50Nm-2 from a volume of 10 m3 to a volume of 4 m3. Energy of 100 J is then added to the gas by heating. Its internal energy is
(a) increased by 400 J
(b) increased by 200 J
(c) increased by 100 J
(d) decreased by 200 J
Question 16:
A sample of gas expands from volume V1 to V2. The amount of work done by the gas is greatest when the expansion is
(a) adiabatic
(b) isobaric
(c) isothermal
(d) equal in all three cases
Question 17:

Question 18:

Question 19:


Question 20:

Question 21:
Find the change in the entropy in the following process 80 g of ice at 0°C melts when dropped in a bucket of water at 50°C. (Assume temperature of water does not change)
(a) – 4.5 calK-1
(b) + 4.5 calK-1
(c) + 5.4 calK-1
(d) – 5.4 calK-1
Question 22:
An ideal gas heat engine operates in Carnot cycle between 227°C and 127°C. It absorbs 6 x104 cal of heat at higher temperature. Amount of heat converted to work is
(a) 2.4 x 104 cal
(b) 6 x 104 cal
(c) 1.2x 104 cal
(d) 4.8 x 104 cal .
Question 23:
Consider a Carnot’s cycle operating between T1 = 500 K and T2 = 300 K producing 1 kJ of mechanical work per cycle. Find the heat transferred to the engine by the.reservoirs.
(a) 1500 J
(b) 1000 J
(c) 2000 J
(d) None of these
Question 24:
A Carnot engine has an efficiency 50% when its sink is at a temperature of 27°C. The temperature of the source is
(a) 273°C
(b) 300°C
(c) 327°C
(d) 373°C
Question 25:
A steam engine whose source is at 400 K, takes 200 cal of heat and rejects 150 cal to the sink. What is the temperature of the sink?
(a) 800 K
(b) 400 K
(c) 300 K
(d) None of these
Question 26:
An engine has an efficiency of 1/6.When the temperature of sink is reduced by 62°C, its efficiency is doubled. Temperature of the source is
(a) 124°C
(b) 37°C
(c) 62°C
(d) 99°C
Question 27:
A Carnot engine whose sink is at 300K has an efficiency of 40%. By how much should the temperature of source be increased so as to increase its efficiency by 50% of original efficiency?
(a) 275 K
(b) 325 K
(C) 250 K
(d) 380 K
Question 28:
A reversible engine takes in heat from a reservoir of heat at 527°C and gives it to the sink at 127°C. How many calorie/s it shall take from the reservoir to do a work of 750 W.
(a) 257 cal s-1
(b) 357 cal s-1
(c) 1500 cal s-1
(d) None of these
Question 29:
In refrigerator one removes heat from a lower temperature and deposits to the surroundings at a higher temperature. In this process, mechanical work has to be done, which is provided by an electrical motor. If the motor is of 1kW power and heat is transferred from -3°C to 27°C, find the heat taken out of the refrigerator per second assuming its efficiency is 50% of a perfect engine.
(a) 12 kJ.
(b) 19 kJ
(c) 10 kJ
(d) 7 kJ
Question 30:
If the coefficient of performance of a refrigerator is 5 and 6 operates at the room temperature (27°C), find the temperature inside the refrigerator.
(a) – 23°C
(b) -20°C .
(c) -15°C
(d) -31 °C
Question 31:


Direction (Q. NOS. 32-36): In each of the following questions a statement of Assertion is given followed by a corresponding statement of Reason just below it. Of the statements mark the correct answer as
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion
(c) If Assertion is true but Reason is false
(d) If both Assertion and Reason are false
Question 32:
Assertion (A):In adiabatic expansion the product of p and V always decreases.
Reason (R):In adiabatic expansion process work is done by the gas at the cost of internal energy of gas.
Question 33:
Assertion (A):It is impossible for a ship to use the internal energy of sea water to operate its engine.
Reason (R):A heat engine is different from a refrigerator.
Question 34:
Assertion (A):Molar heat capacity cannot be defined for isothermal process.
Reason (R):In isothermal process p-V versus T graph is a dot.
Question 35:
Assertion (A):Specific heat capacity is the cause of formation of land and sea breeze.
Reason (R):The specific heat of water is more than land.
Question 36:
Assertion (A):It is hotter over the top of a fire than at the same distance of the side.
Reason (R):In the upward direction the heat propagate through convection.
Question 37:
Ten moles of an ideal gas at constant temperature 600 K is compressed from 100L to 10L. The work done in the process is
(a) 4.11 x 104 J
(b) -4.11 x 104 J
(c) 11.4 x 104 J
(d) -11.4 x 104 J
Question 38:


Question 39:
A Carnot engine, having an efficiency of η= 1/10 as heat engine is used as a refrigerator. If the work done on the system is 10 J, the amount of energy absorbed from the reservoir at lower temperature is
(a) 100 J
(b) 99 J
(c) 90 J
(d) 1 J
Question 40:

Question 41:

Question 42:
A monoatomic gas at a pressure p, having a volume V expands isothermally to a volume 2V and then adiabatically to a volume 16v. The final pressure of the gas is (take γ = 5/3)
(a) 64p
(b) 32p
(c) p/64
(d) 16p
Question 43:

Question 44:
During an adiabatic process, the pressure of a gas is found to be’ proportional to the cube of its temperature. The ratio of Cp/Cv for the gas is
(a) 4/3
(b) 2
(c) 5/3
(d) 3/2
Question 45:

Question 46:

Question 47:
If for hydrogen Cp -Cv =m and for nitrogen Cp-Cv =n where, Cp and Cv refer to specific heat per unit mass respectively at constant pressure and constant volume, the relation between m and n is (Molecular weight of hydrogen =2 and molecular weight of nitrogen = 28)
(a) n = 14m
(b) n = 7m
(c) m = 7n
(d) m = 14n
Question 48:

Question 49:
An ideal refrigerator has a freezer at a temperature of – 13°C. The coefficient of performance of the engine is 5. The temperature of the air (to which heat is rejected) will be
(a) 325°C
(b) 325 K
(c) 39°C
(d) 320°.C
Question 50:
Which of the following statements is correct for any thermodynamic system?
(a) The internal energy changes in all processes
(b) Internal energy and entropy are state functions
(c) The change in entropy can never be zero
(d) The work done in an adiabatic process is always zero
Question 51:
Assertion (A):A thermoelectric refrigerator is based on the Peltier effect.
Reason (R):A thermocouple may be used as a radiation detector.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion
(c) If Assertion is true but Reason is false
(d) If both Assertion and Reason are false
Question 52:
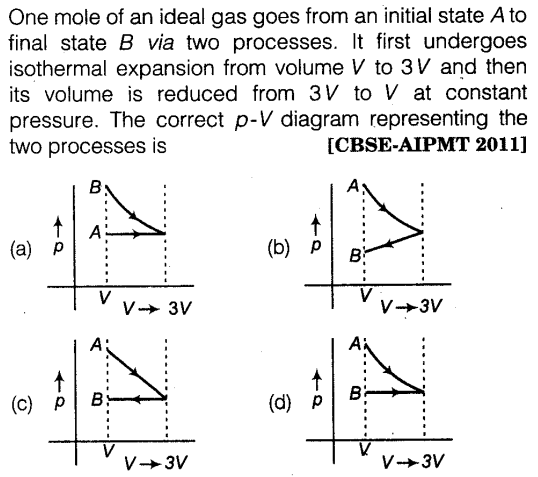
Question 53:

Question 54:

Question 55:
We consider a thermodynamic system. If ΔU represents the increase in its internal energy and W the work done by the system, which of the following statements is true?
(a) ΔU = – W in an adiabatic process
(b) ΔU = W in an isothermal process
(c) ΔU = – W in an isothermal process
(d) ΔU = W in an adiabatic process
Answers:

Hints And Solutions: