These Sample papers are part of CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science. Here we have given CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Paper 15.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Paper 15
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | X |
| Subject | Social Science |
| Sample Paper Set | Paper 15 |
| Category | CBSE Sample Papers |
Students who are going to appear for CBSE Class 10 Examinations are advised to practice the CBSE sample papers given here which is designed as per the latest Syllabus and marking scheme as prescribed by the CBSE is given here. Paper 15 of Solved CBSE Sample Paper for Class 10 Social Science is given below with free PDF download solutions.
Time Allowed: 3 hours
Max. Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- This question paper consists of 28 questions in all. All questions are compulsory.
- Questions from Serial No. 1 to 7 are very short answer type questions. Each question carries 1 mark.
- Questions from Serial No. 8 to 18 are of 3 marks questions. Answer to these questions should not exceed 80 words each.
- Questions from Serial No. 19 to 25 are of 5 marks questions. Answer should not exceed 100 words each.
- Questions No. 26 and 27 are map questions carrying 1+1= 2 marks from History. After completion, attach the maps inside your answer books.
- Questions No. 28 is a map question of 3 marks from geography.
Question 1.
What was the strong demand of the emerging middle classes in Europe during 19th Century?
OR
What was the result of peace negotiations in Geneva that followed the french defeat in Vietnam?
Question 2.
How did business classes relate to CDM?
OR
Who was Ho Chi Minh?
Question 3.
What kind of government is there in Brussels?
Question 4.
Give examples of holding together federation?
Question 5.
On which factor does the outcome of politics of social division depends?
Question 6.
Why do different people have different developmental goals?
Question 7.
Which people are vulnerable in unorganised sector of urban area?
Question 8.
How did Indian Entrepreneurs survive despite tight economic controls imposed by the British Government?
OR
Explain any three major problems faced by the people who migrated to Bombay during the 19th Century.
Question 9.
Give three types of arguments on the effects of print technology on French Revolution.
OR
Examine those factors that enabled the people have easier and greater access to books in the 18th century?
Question 10.
Explain the ecological problems being faced due to multipurpose river valley project.
Question 11.
Mention the geographical requirements for the growth of wheat in India. Mention two wheat growing zones.
Question 12.
What is the need of using Non-conventional sources of energy?
Question 13.
Give any three provisions of the Indian constitution which make India a full fledged federalism.
Question 14.
How can a relationship between religion and politics be established?
Question 15.
Suggest some reforms to strengthen parties so that they perform their functions well.
Question 16.
How is the tertiary sector different from the other sectors? Illustrate with a few examples.
Question 17.
How is the money transferred from one bank account to another bank account? Explain with an example.
Question 18.
“A wide ranging choice of goods are available in the Indian markets”. Support the statement with an example in context of globalisation.
Question 19.
How did the Polish language work as a symbol of struggle against Russian dominance.
OR
What was the condition of colonial economy in Vietnam. Explain elaborately.
OR
Why did Mahatma Gandhi decide to call off the Civil Disobedience Movement? Explain.
Question 20.
Assess the role of Mahatma Gandhi in the Nationalist Movement with special reference to the methods adopted by him.
OR
Explain factors which gave rise to the civil Disobedience Movement of 1930.
Question 21.
Why have the demand of Jute products increased internally as well as globally?
Question 22.
Discuss the significance of National Highways and Border roads.
OR
Describe the nature and role of feature films in India.
Question 23.
Why was Brussels chosen as headquarters during the formation of European Union?
Question 24.
Explain three different types of challenges being faced by democratic governments in modern times.
OR
How challenge of language policy was adopted by the Indian federalism?
Question 25.
What are the drawbacks of Consumer Movement in India?
OR
Have you heard of consumer forums? If yes, write’its significance according to you. ‘
Question 26.
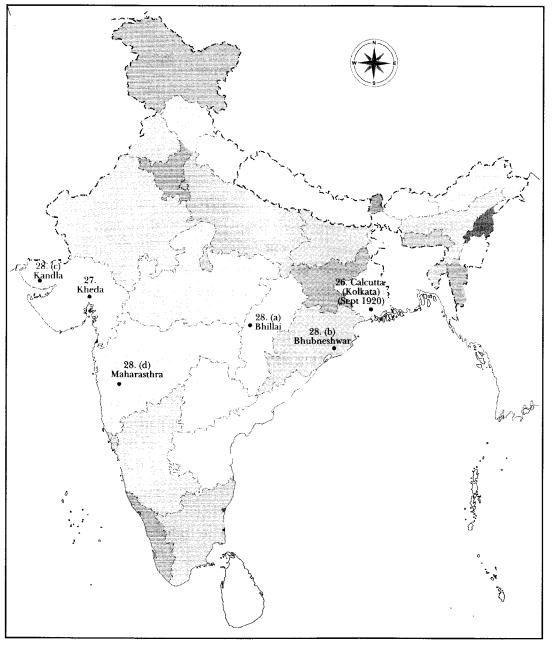
On the given outline map of India, locate and mark the place where Congress Session of September 1920 held.
Question 27.
On the given outline map of India, locate and mark the place where peasants went on Satyagrah.
Question 28.
On the given political map of India identify the following:
(a) An Iron and Steel plant.
(b) A Software Technology Park.
(c) An important sea port.
(d) Major sugarcane producing state.
Answers
Answer 1.
The strong demand of emerging middle class in Europe was freedom of markets and the abolition of state imposed restrictions on the movement of goods and capital.
OR
The result of the peace negotiations in Geneva that followed the French defeat in Vietnam was: Division of Vietnam into North and South Vietnam with different ideologies.
Answer 2.
Business classes wanted protection against imports of foreign goods and a rupee-sterling foreign exchange ratio that would discourage imports. They now reacted against colonial policies that restricted business activities.
OR
Ho Chi Minh brought together the competing nationalist groups to establish the Vietnamese communist party, later renamed as the Indo-Chinese Communist Party. He was inspired by the militant demonstrations of the European Communist Parties.
Answer 3.
Brussels has a separate government in which both the communities have equal representation. The French speaking people accepted equal representation in Brussels because the Dutch speaking community has accepted equal representation in the Central Government.
Answer 4.
India, Spain and Belgium are examples of holding together federations. In it, the central government lends to be more powerful vis-a-vis the states.
Answer 5.
The outcome depends on how people perceive their identities. If people see their identities in singular and exclusive terms, it becomes very difficult to accommodate.
Answer 6.
Different people have different developmental goals because different people have different wishes, likes and dislikes and aspirations.
Answer 7.
In the urban areas, unorganised sector comprises mainly of workers in small- scale industry, casual workers in construction, trade and transport etc. and those who work as street vendors, head load workers, garment makers, ragpickers etc. are vulnerable so they need to be protected.
Answer 8.
Indian entrepreneurs survived despite strict economic controls by the British Government due to following reasons:
- In the late 19th century when Indian entrepreneurs started setting up Industries, they avoided competing with Manchester goods, in the Indian market.
- The early cotton mills in Indian produced coarse cotton yarn, rather than fabric because yarn was not an important part of British imports to India. When yarn was imported it was of superior quality.
- The yarn produced in the Indian spinning mills was either exported to China or used by the handloom weavers in India which maintained the demand and supply.
OR
The problems faced by migrants to Bombay during the 19th century were:
- Housing problem and water scarcity became acute in the 1850’s. New textile mills increased the problem as more and more labour was migrating to Bombay. Since water was scarce, people quarreled every morning for a turn at the tap.
- More than 70 per cent of the working class lived in Chawls. Chawls were one room tenements which were shared by many family members. There were filthy gutters, buffalo stables etc. very close to the chawls.
- Since the houses were small, streets and neighbourhood were used for cooking, washing and sleeping too. Akharas and liquor shops too emerged in the neighbourhood.
Answer 9.
- The ideas of enlightenment thinkers: Collectively their writings provided a critical commentary on tradition, superstition and despotism. People argued for the rule of reason rather than custom and demanded that everything be judged through the application of reason and rationality. The writings of voltair and Rousseau were read widely those who read these books saw the world through new eyes.
- Print created a new culture of dialogue and debate: People had become aware of the power of reason and recognised the need to question existing ideas and beliefs. So new ideas of social revolution came into being.
- There was an outpouring of literature that mocked the royality and criticised their morality: Many cartoons and caricatures suggested that monarchy enjoys its own comforts, while common people suffered. The literature was circulated underground and led to the growth of hostile sentiments against the monarchy.
OR
The factors which enabled the people to have easier and greater access to books in the 18th century were:
- Introduction of a system of libraries which gave access to the poor people also to borrow and read a book.
- Printing press brought down the prices of books.
- People started hiring for the number of hours as per the need.
- Now those who could not afford to buy books could borrow them.
Answer 10.
- Regulating and damming of rivers affect their natural flow causing poor sediment flow and excessive sedimentation at the bottom of reservoirs.
- It results in rocky streams beds and poorer habitats for the rivers aquatic life.
- Dams also fragment rivers making it difficult for aquatic fauna to migrate, especially for spawning (laying of eggs).
- The reservoirs that are created on the flood plains also submerge the existing vegetation and soil, leading to its decomposition over a period of time.
Answer 11.
- Wheat is one of the most important cereal crop of India.
- This rabi crop requires a cool growing season and a bright sunshine at the time of ripening.
- It requires 50 to 75 cms of annual rainfall evenly distributed over the growing season. Two wheat growing zones are:
- Ganga-Satluj plain in the north-west.
- The black soil region of the Deccan.
Answer 12.
Need of using non-conventional sources of energy:
- The growing consumption of energy has resulted in the country becoming increasingly dependent on fossil fuels such as coal, oil and gas.
- Rising prices of oil and gas and their potential shortages have raised uncertainties about the security of energy supply in future, which has serious repercussions on the growth of the national economy.
- Increasing use of fossil fuels also causes serious environmental problems. Hence there is a primary need to use renewable sources like solar, wind, tidal, biomass and energy from waste material. They all called non-conventional sources of energy.
Answer 13.
- There are two or more levels of government.
- Different tiers of government govern the same citizens, but each tier has its own jurisdiction.
- The jurisdiction of the respective levels or tiers of government are specified in the constitution.
- The fundamental provisions of the constitution cannot be unilaterally changed by one level of the government.
- Sources of revenue for each level of government are clearly specified to ensure its financial autonomy.
- Courts have the power to interpret the constitution and the powers of different levels of government.
Answer 14.
The relationship between religion and politics can be established by setting up following constitutional provisions:
- There is no official religion. The Indian Constitution does not give special status to any religion.
- The constitution provides to all individuals and communities freedom to practice and propagate any religion, or not to follow any.
- At the same time, the constitution allows the state to intervene in matters of religion in order to ensure equality within religious communities.
Answer 15.
Reforms to strengthen Parties are:
- There has to be mechanism to check that the information given by a candidate for elections in his affidavit is correct and true.
- There has to be a mechanism for elected members to dissent without needing to detect loosing their seat.
- Internal elections have to be held for all decision making positions of a party with a transparent list of voters.
- Initiatives have to be taken to stop the flow of illegal money to political parties during elections.
Answer 16.
- The other sectors provide a product whereas the tertiary sector do not produce a good but they are aid or support for the production process.
- For example: goods that are produced in primary and secondary sector would need to be transported by trucks or trains and then sold in the wholesale and retail shops.
- Transport, storage, communication, banking and trade are few examples of tertiary activities.
- Since these activities generate services rather than goods the tertiary sector is also known as the service sector.
Answer 17.
If a person has to make payment to his or her friend and writes a cheque for a specific amount, this means that the person instructs his bank to pay this amount to his friend. His friend takes this cheque and deposits it in his account in the bank. This said amount is transferred from one bank account to another bank account.
Answer 18.
- We have a wide variety of goods and services before us in the market.
- The latest models of the digital cameras, mobile phones and televisions made by leading manufacturers of the world are available in the market.
- Every season, new models of automobiles can be seen on Indian roads.
- Today Indians are buying cars produced by nearly all the top companies in the world.
- A similar explosion of brands can be seen for many other goods.
Answer 19.
Language too played an important role in developing nationalist sentiments:
- After Russian occupation, the polish language was forced out of schools and the Russian language was imposed everywhere.
- In 1831, an armed rebellion against Russian rule took place which was ultimately crushed.
- Following this, many members of the clergy in Poland began to use language as a weapon of national resistance.
- Polish was used for church gatherings and all religious instructions.
- As a result, a large number of priests and bishops were put in jail or sent to Siberia by the Russian authority as punishment for their refusal to preach in Russia.
- The use of Polish came to be seen as a symbol of the struggle against Russian dominance.
OR
- The colonial economy in Vietnam was, however primarily based on rice cultivation and rubber plantations owned by the French and a small Vietnamese elite.
- Rail and port facilities were set up to service this sector; indentured labour was widely used in the rubber plantations.
- The French contrarily to what Bernard would have liked, did little to industrialise the economy.
- In the rural areas landlordism spread and the standard of living declined.
- The vast system of irrigation work, canals and earthworks built mainly with forced labour, increased rice production and allowed the export of nice to International market.
OR
Mahatma Gandhi decided to call off civil Disobedience Movement because:
- Worried by the development of civil Disobedience movement the colonial government began arresting the congress leaders one by one.
- This led to violent cluster in many places.
- When Khan Abdul Gaffar Khan, a devoted disciple of Mahatma Gandhi was arrested (April 1930) angry crowds demonstrated in the street of Peshawar, facing armored cars and police firing. Many were killed.
- A month later, when Mahatma Gandhi was arrested industrial workers in sholapur attacked police force municipal building, law courts, railway stations and all other structures that symbolised British rule.
- A frightened government responded with the policy of brutal repression.
- The peaceful satyagrahi were attacked, women and children were beaten and about 1 lakh people were arrested.
Under these circumstances Mahatma Gandhi called off the Civil Disobedience Movement.
Answer 20.
Gandhiji played a leading role in the Indian National Movement from 1916 till Independence.
- He believed in Satyagraha and non-violence, so he successfully involved masses in the Satyagraha movements in Champaran, Kheda and Ahmedabad to raise the voice of peasants and workers.
- Only he could organise mass movements like Non-cooperation, Civil Disobedience and Quit India movements to pressurise the colonial government to withdraw from India and get Independence.
- He mobilised the people to unite only their feeling of nationalisms can be awakened. He was supported by people from all walks of life.
- He cleaned toilets himself to give respect and dignity to depressed classes and he called them ‘Harijans’ as god’s people.
- His unique method of satyagraha based on non-violence was appreciated by one and all and even by Britishers. In his famous movements he regulated Indians to boycott British goods and opt for Khadi and indigenous goods, picketed shops selling foreign goods, non-payment of taxes and boycotting British Institutes, Courts or Schools or Colleges to show protest.
OR
Factors which gave rise to Civil Disobedience Movement are:
- Worldwide economic depression: As a result of worldwide economic depression before World War-II, agricultural prices began to fall in India. The demand for agricultural goods declined and export decreased. The peasants could not sell their harvest and it became difficult for them to pay land revenue.
- Simon Commission: In 1928, Simon Commission was constituted to look into the functioning of constitutional system in India and suggest some legislative reforms. However, as no Indian member was appointed, it was opposed by all political parties by holding demonstrations.
- Dominion Status’s announcement by Lord Irwin: Lord Irwin announced in October 1929 that dominion status would be granted to India in an unspecified future and a Round Table conference to discuss a future constitution would take place.
- Declaration at Lahore Congress Session, 1929: At Lahore Congress Session under the Presentship ofjawahar Lai Nehru, resolution for ‘Purna Swaraj or total Independence was passed. Gandhiji was authorised to start a movement for the achievement of ‘Purna Swaraj’. Thus salt March was started.
Answer 21.
The demand for Jute products increased internally as well as globally due to following reasons:
- Jute is a biodegradable product and due to invasion of plastics, Jute is needed for being environment friendly.
- Many countries want to get rid of plastic bags and want to replace it with environment friendly jute bags.
- Jute industry also support a large number of marginal farmers who are engaged in cultivation of Jute and Mesta in the countries like India and Bangladesh.
- Internal demand has increased in India due to the government’s policy of jute packaging.
- Recently jute has also been mixed with cotton to manufacture cloth.
Answer 22.
Significance of National Highways:
- National Highways are the major route system of India.
- They link extreme parts of the country and provide connectivity between the different states of India.
- They have been planned to meet the requirements of fast movement of traffic in the country.
- They connect most of the important towns and cities of the country.
- The National Highways are laid by CPWD or Central Public Works Department.
- National Highway Authority of India (NHAI) is responsible for constructing Super Highways and Expressways in India.
Border Roads:
- The border roads provide a link to the border frontiers and towns of our country.
- These roads are required by around forces to access and protect India’s border.
- The border road organisation under the government of India constructs and maintains these roads.
OR
Role of Feature films
- India is the largest producer of short films, feature films and video short films.
- The Central Board of film certification is the authority to certify both Indian and regional films and foreign films too.
- It is one of the mass communications which provides entertainment, education and creates awareness among the people.
- Feature films are made on the topics of nationality, culture, family system and social issues.
- In India films are made in Hindi as well as all regional languages which are spoken in different states of India.
Answer 23.
- Belgian leaders recognised the existence of’regional differences and cultural diversities.
- Between 1970 and 1993, they amended their constitution four times, so as to work out an arrangement that would enable everyone to live together within the same country.
- This arrangement was different from any other country and was very innovative, such as they put the equal no. of ministers in the central government from Dutch and French speaking both.
- They formed a community government which would be empowered to take up cultural, educational and language related issues of their community.
Answer 24.
Following are the types of Challenges being faced by modern democracies in the world.
- Foundational Challenge:
- Foundational challenge takes place when the basic structure or foundation of the government changes.
- It can be monarchy or military dictatorship, changed into democracy.
- Deepening of Democracy:
- This involves strengthening of the institutions and practices of democracy.
- This should happen in such a way that people can realise their expectations of democracy.
- This requires an attempt to bring down the control and influence of the rich and powerful people in waking governmental issue.
- Challenge of Expansion
- This involves applying the basic principle of democratic government across all regions, different social groups and various institutions.
- Ensuring greater power to local government execution of federal principle to all the units of federation, inclusion of women and minority group, etc. fall under this challenge.
This also means that less decisions should remain outside the area of democratic control.
OR
- A second test for Indian federalism is the language policy.
- Our Constitution did not give the status of national language to any one language.
- Hindi was identified as the official language.
- But Hindi is the mother tongue of only about 40 per cent of Indians. Therefore, there were many safeguards to protect other languages.
- Besides Hindi, there are 21 other languages recognised as Scheduled Languages by the Constitution.
- A candidate in an examination conducted for the Central Government positions may opt to take the examination in any one of these languages.
- States too have their own official languages. Much of the government work takes place in the official language of the concerned state.
Answer 25.
- The consumer redressal process is becoming cumbersome, expensive and time consuming.
- Many times, consumers are required to engage a lawyer.
- The cases require time for filing and attending the court proceedings etc.
- In most purchases, cash memos are not issued, hence evidence is not easy to gather.
- Moreover, most purchases in the market are small retail sales.
- The existing laws also are not very clear on the issue of compensation to consumers injured by defective products.
- After 25 years of the enactment of COPRA, consumer awareness in India is spreading but slowly.
- Besides this, the enforcement of laws that protects workers, especially in the unorganised sector is weak.
- Rules and regulations for the functioning of markets are often not followed.
OR
- The consumer movement in India has led to the formation of various organisations locally known as consumer Forums or Consumer Protection Council.
- Following are the functions of Consumer Forums:
- They guide consumers on how to file cases in the consumer courts.
- On many occasions, they represent individual consumers in the consumer courts.
- They work for protection of consumer rights.
- They impact knowledge about consumer rights by writing articles and getting it published in the newspapers.
Answer 26.

Answer 27.

Answer 28.
We hope the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Paper 15 help you. If you have any query regarding CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Paper 15, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.