CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 3 are part of CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry. Here we have given CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 3.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 3
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | XII |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Sample Paper Set | Paper 3 |
| Category | CBSE Sample Papers |
Students who are going to appear for CBSE Class 12 Examinations are advised to practice the CBSE sample papers given here which is designed as per the latest Syllabus and marking scheme, as prescribed by the CBSE, is given here. Paper 3 of Solved CBSE Sample Paper for Class 12 Chemistry is given below with free PDF download solutions.
Time Allowed : 3 Hours
Max. Marks: 70
General Instructions
- All questions are compulsory.
- Question number 1 to 5 are very short answer questions and carry 1 mark each.
- Question number 6 to 10 are short answer questions and carry 2 marks each.
- Question number 11 to 22 are also short answer questions and carry 3 marks each.
- Question number 23 is a value based question and carry 4 marks.
- Question number 24 to 26 are long answer questions and carry 5 marks each.
- Use log table, if necessary. Use of calculators is not allowed.
Questions
Question 1.
Write the IUPAC name of the K3[Fe(CN)6].
Question 2.
Out of cyclohexanol and phenol which is more acidic?
Question 3.
Define half life period (t1/2).
Question 4.
Why is tyndall effect shown by colloidal solution?
Question 5.
What are micelles?
Question 6.
Explan the following terms with suitable example:
- F-centres
- Schottky defect
Question 7.
Define osmotic pressure. How is osmotic pressure related to the concentration of a solute in the solution?
Question 8.
What happens when:
- Concentrated HNO3 is added to I2.
- SO3 is passed through water.
Question 9.
- Name the element which should not be considered as transition element.
- Cr2+ is stronger reducing agent as compared to Mn2+.
Question 10.
(i) Which compound in each of the following pairs will react faster in SN1 reaction.
(a) CH3-CH = CHCl or CH2 = CH-CH2Cl

OR
Carry out following conversions (in not more than 2 step)
(i) Bromobutane from but-1-ene
(ii) Biphenyl from benzene
Question 11.
An element exists in fee arrangement, having density 4.2 g/cm3 and radius of its atom is 141.4 pm. Find molar mass of this element (NA = 6.022 × 1023).
Question 12.
Find mass of glycol required to run a car at a hill station having temperature -10°C and radiator of car can accommodate 5L of liquid. Kf for water is 1.86K kg mol-1 and molar mass of glycol is 62 g/mol.
Question 13.
The rates of most reactions double when their temperature is raised by 10°C. Find activation energy for the reaction if temperature of reaction raised from 300 K to 320 K.
Question 14.
Describe the preparation of KMnO4. How does it reacts with KI in alkaline medium.
Question 15.
Discuss the hybridisation and magnetic behaviour of [Co(NH3)6]3+ according to valence bond theory.
Question 16.
Explain following named reaction with a suitable example
- Reimer Tiemann Reaction
- Williamson synthesis
- Tran-sestrification
Question 17.
Explain the following terms:
- Brownian movement
- Zeta potential
- Coagulation
Question 18.
Write reactions involved in the following pairs:
(i) CH3CH2Cl is treated with alcoholic KOH
(ii) CH3Cl is treated with NaNO2
(iii) CH3Cl is treated with AgCN.
Question 19.
Outine the principles involved in following process:
- Chromatography
- Distillation
- Liquation
Question 20.
Write the products A and B in the following:

Question 21.
Write two uses of each of the following polymers:
- Teflon
- Nylon 6,6
- Nylon-2 – Nylon-6
Question 22.
What are enzymes? Describe their functions. Name two diseases which are caused due to deficiency of enzymes.
Question 23.
Ankit’s grandfather is not only obese but he is also a diabetic patient. Seeing his fondness for sweets, Ankit suggested him to replace sugar with artificial sweeteners. After few days, Ankit observed a controlled level of sugar in his grandfather.
Answer the following:
- What are the values displayed by Ankit?
- What are artificial sweeteners?
- Give two examples of artificial sweeteners.
- Name an artificial sweetener which is unstable at cooking temperature.
Question 24.
(a)
- Write reaction of discharging of lead storage batteries.
- Write its two disadvantages.
(b) Chromium metal can be plated from acidic solution of CrO3. Reaction is as follows:
CrO3(aq) + 6H+ + 6e– → Cr(s) + 3H2O
Calculate mass of Cr plated by 24,000 coulombs of electricity and find the time required in deposition of 1.3 g chromium by using a current of 20 ampere?
(Molar mass of Cr = 52 g/mol)
OR
Answer the following questions:
- What is corrosion?
- Define fuel cell.
- State Kohlrausch law.
(b) Calculate ΔrG° for the following reaction at 298 K.
Cu(s) + 2Ag+(aq) \(\rightleftharpoons\) Cu2+(aq) + 2Ag(s)
Given E0cell = 0.46V
Question 25.
(a) Draw the structures of
(i) XeOF4
(ii) H3PO3
(b) What happens when
(i) PCl5 is heated?
(ii) White phosphorous is heated with NaOH solution in an inert atmosphere of CO2?
(iii) H3PO3 is heated?
OR
(a) Give reason for the following:
- CN– ion is known but CP– is not known.
- H2S is more acidic than H2O.
(b) Arrange the following in increasing order of property indicated:
- F2, Cl2, Br2, I2 (Bond dissociation enthalpy)
- HF, HCl, HBr, HI (acidic strength)
- NH3, PH3, AsH3, SbH3, BiH3 (Basic strength)
Question 26.
(a) Complete the following equations

(b) Distinguish between following species with a suitable chemical test:

OR
(a) Explain the following ternis by taking up a suitable reaction:
(i) Semi carbazone
(ii) Ketal
(b) Complete the following reactions:
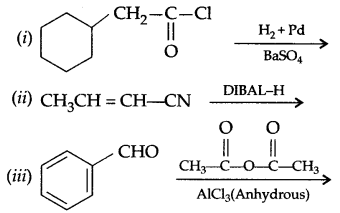
Answers
Answer 1.
Potassium hexacyanidoferrate (III)
Answer 2.
Phenol due to resonance stabilisation of phenoxide ion.
Answer 3.
The time in which half of the reactant get converted into product is known as half life (t1/2).
Answer 4.
Particles of dispersed phase scatter light hence tyndall effect is shown by colloidal solution.
Answer 5.
The soap solution in water after a certain concentration of soap, known as critical micelle concentration (CMC) forms associated colloid also known as “Micelles”.
Answer 6.
- F-centre: In metal excess defect, the points in which electron is present in place of negative ion (anion) is known as f-centre.
- Schottky defect: The defect present in ionic solid (having comparable size of cation and anion) in which equal number of cation and anion are missing from the crystal lattice is known as schottky defect.
Answer 7.
Osmotic pressure: The pressure applied on higher concentration side of semipermeable membrane so that there is no net flow of solvent in either side of membrane is known as osmotic pressure.
It is directly proportional to concentration of solution.
π = CRT where C is concentration in mol/L
Answer 8.
- 10HNO3 + I2 → 2HIO3 + 10NO2 + 4H2O
- SO3 + H2O → H2SO4
Answer 9.
- Zn, Cd and Hg
- Cr2+ is less stable than Cr3+ (half filled t2g orbital), hence Cr2+ acts as reducing agent and likely to get oxidised to Cr3+. On the other hand Mn2+ has half filled d orbital, hence it is more stable than Mn3+, so it is not likely to get oxidised.
Answer 10.
(i) (a) CH2 = CH – CH2Cl (due to stabilisation of cation through conjugation)

Answer 11.
From given information
Z = 4, d = 4.2 g/cm3, r = 141.4 pm, m = ?
For fcc arrangement


Answer 12.
ΔTf = 10K (-10°C = 263K, 0°C = 273 K so ΔTf = 10 K)
Volume of radiator = 5 L = 5000 mL = 5000 g
wB (mass of glycol) = ?
mB = 62 g/mol
Kf = 1.86 K kg mol-1
i = 1 for glycol.
ΔTf = iKfm

wB 1666.67 g
Mass of glycol need to be added = 1666.67 g
Answer 13.
On 20°C rise in temperature rate will increase four times i.e. K1 = K then K2 = 4 K From Arrhenius equation,

Answer 14.
preparation of KMnO4 :

Answer 15.
Cobalt is in +3 oxidation state in [Co(NH3)6]3+.
Orbital electronic configuration of Co3+ – 3d6


Answer 16.
1. Reimer Tiemann Reaction: It is the reaction of phenol with chloroform in aqueous alkali at 60°C to introduce an aldehydic group at ortho position of the benzene ring.

2. Williamson Synthesis: It is the reaction for ester synthesis by attack of an alkoxide on alkyl halide.
![]()
3. Trans-esterification: Alkoxy group present in ester get exchanged with another alcohol. This reaction is known as trans-esterffiction.

Answer 17.
- Brownian movement: The zig-zag movement of colloidal particles in dispersion medium due to constant bombardment of these particles by molecules of dispersion medium is called Brownian movement.
- Zeta potential: The potential difference between fixed layer and diffused layer of opposite charges is called beta potential or electrokinetic potential.
- Coagulation: The process of aggregation of colloidal particles in an insoluble precipitate by the addition of suitable electrolyte is called coagulation.
Answer 18.

Answer 19.
- Chromatography: The principle involved is different adsorbability of different components of solution on stationary phase.
- Distillation: The principle involved is different boiling point of different components i.e. metal and impurity.
- Liquation: In this method the principle involved is lower melting point of metal as compared to impurity and impurity should not be miscible with metal.
Answer 20.


Answer 21.
| Name of polymer | Use of polymer |
| (1) Teflon | Electrical insulation and non-stick cookwares. |
| (2) Nylon 6, 6 | Sheets, parachutes, bristles of brushes. |
| (3) Nylon-2-Nylon-6 | Dissolvable sutures, biodegradable polyamide |
Answer 22.
Enzymes are proteins which act as biochemical catalyst and increase rate of reactions efficiently and specifically. Disease caused by enzyme deficiency.
- Phenylketonurea: Caused by deficiency of enzyme phenyl alanine hydroxylase.
- Albinism: Due to deficiency of enzyme tyrosinase.
- Steptokinase: Dissolves blood clot formed in coronary artery which leads to heart trouble.
Answer 23.
- Scientific knowledge and critical thinking.
- The sweetening agent which provides sweet taste but not have any calorific value are known as artificial sweeteners.
- Sucralose, Alitame
- Aspartame
Answer 24.
(a)
- Pb(s) + PbO2(s) + 2H2SO4(aq) → 2PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(l)
- It releases SO2 gas harmful for health.
- Its disposal causes environment pollution.
- Life of such cells are short.

OR
(a)
- Corrosion: The process of slow eating up of metal by gases and water vapours present in atmosphere due to the formation of certain compounds like oxides, sulphides, carbonates etc is called corrosion.
- Fuel cell: The cells which produce electrical energy directly from the combustion of fuel such as H2, CH3OH, CH4 etc.
- Kohlrausch law: It states that the limiting molar conductivity of an electrolyte can be represented as the sum of the individual contributions of the anion and cation of the electrolyte. If an electrolyte on dissociation give υ+ cations and υ– anions, then
- Δ0m= υ+λ0+ + υ–λ0–
Here λ0+ and λ0– are the limiting molar conductivity of cation and anion respectively.
(b) Here n = 2
ΔrG° – -nFE0cell
= -2 × 96500 × 0.46 J
= – 88780 J = -88.78 kJ
Answer 25.

OR
(a)
- Nitrogen being smaller in size can form pπ-pπ multiple bond with carbon, so CN– ion can form but phosphorous cannot form pπ-pπ bond due to larger size of P, so CP– is not possible.
- This is because bond enthalpy of H-S bond is lower than O-H bond.
(b)
- I2 < F2 < Br2 < Cl2
- HF < HCl < HBr < HI
- BiH3 < SbH3 < AsH3 < PH3 < NH3.
Answer 26.



We hope the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 3 help you. If you have any query regarding CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Paper 3, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.