NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths Chapter 4 Determinants Ex 4.6 are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths 4 Determinants Ex 4.6.
- Determinants Class 12 Ex 4.1
- Determinants Class 12 Ex 4.2
- Determinants Class 12 Ex 4.3
- Determinants Class 12 Ex 4.4
- Determinants Class 12 Ex 4.5
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 12 |
| Subject | Maths |
| Chapter | Chapter 4 |
| Chapter Name | Determinants |
| Exercise | Ex 4.6 |
| Number of Questions Solved | 16 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths Chapter 4 Determinants Ex 4.6
Examine the consistency of the system of equations in Questions 1 to 6:
Ex 4.6 Class 12 Maths Question 1.
x + 2y = 2
2x + 3y = 3
Solution:
x + 2y = 2,
2x + 3y = 3
=> \(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 2 \\ 2 & 3 \end{bmatrix}\left[ \begin{matrix} x \\ y \end{matrix} \right] =\left[ \begin{matrix} 2 \\ 3 \end{matrix} \right] \)
=> AX = B
Now |A| = \(\begin{vmatrix} 1 & 2 \\ 2 & 3 \end{vmatrix}\)
= 3 – 4
= – 1 ≠ 0.
Hence, equations are consistent.
Ex 4.6 Class 12 Maths Question 2.
2x – y = 5
x + y = 4
Solution:
2x – y = 5,
x + y = 4
=> \(\begin{bmatrix} 2 & -1 \\ 1 & 1 \end{bmatrix}\left[ \begin{matrix} x \\ y \end{matrix} \right] =\left[ \begin{matrix} 5 \\ 4 \end{matrix} \right] \)
=> AX = B
Now |A| = \(\begin{vmatrix} 2 & -1 \\ 1 & 1 \end{vmatrix}\)
= 2 + 1
= 3 ≠ 0.
Hence, equations are consistent.
Ex 4.6 Class 12 Maths Question 3.
x + 3y = 5,
2x + 6y = 8
Solution:
x + 3y = 5,
2x + 6y = 8
=> \(\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 3 \\ 2 & 6 \end{bmatrix}\left[ \begin{matrix} x \\ y \end{matrix} \right] =\left[ \begin{matrix} 5 \\ 8 \end{matrix} \right] \)
=> AX = B
Now |A| = \(\begin{vmatrix} 1 & 3 \\ 2 & 6 \end{vmatrix}\)
= 6 – 6
= 0.

Hence, equations are consistent with no solution
Ex 4.6 Class 12 Maths Question 4.
x + y + z = 1
2x + 3y + 2z = 2
ax + ay + 2az = 4
Solution:
x + y + z = 1
2x + 3y + 2z = 2
x + y + z = \(\\ \frac { 4 }{ a } \)

Ex 4.6 Class 12 Maths Question 5.
3x – y – 2z = 2
2y – z = – 1
3x – 5y = 3
Solution:
\(\left[ \begin{matrix} 3 & -1 & -2 \\ 0 & 2 & -1 \\ 3 & -5 & 0 \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix} x \\ y \\ z \end{matrix} \right] =\left[ \begin{matrix} 2 \\ -1 \\ 3 \end{matrix} \right] \)
=> AX = B

Ex 4.6 Class 12 Maths Question 6.
5x – y + 4z = 5
2x + 3y + 5z = 2
5x – 2y + 6z = -1
Solution:
Given
5x – y + 4z = 5
2x + 3y + 5z = 2
5x – 2y + 6z = -1
\(\left[ \begin{matrix} 5 & -1 & 4 \\ 2 & 3 & 5 \\ 5 & -2 & 6 \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix} x \\ y \\ z \end{matrix} \right] =\left[ \begin{matrix} 5 \\ 2 \\ -1 \end{matrix} \right] \)
\(AX=B|A|=\left[ \begin{matrix} 5 & -1 & 4 \\ 2 & 3 & 5 \\ 5 & -2 & 6 \end{matrix} \right] \)
= 5(18 + 10)+1(12 – 25)+4(-4-15)
= 140-13-76
= 51 ≠ 0
Hence equations are consistent with a unique
solution.
Solve system of linear equations using matrix method in Questions 7 to 14:
Ex 4.6 Class 12 Maths Question 7.
5x + 2y = 4
7x + 3y = 5
Solution:
The given system of equations can be written as
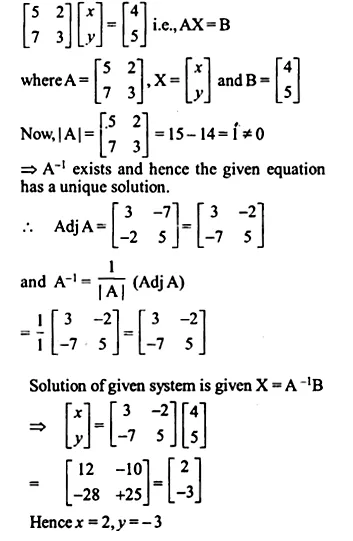
Ex 4.6 Class 12 Maths Question 8.
2x – y = – 2
3x + 3y = 3
Solution:
The given system of equations can be written
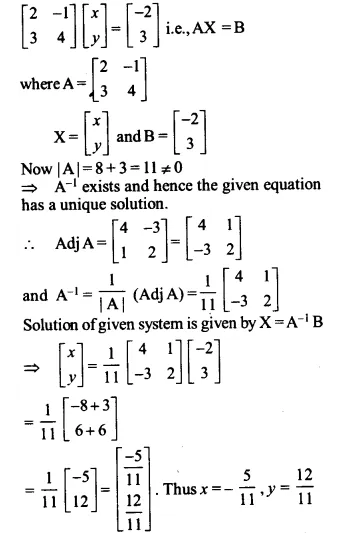
Ex 4.6 Class 12 Maths Question 9.
4x – 3y = 3
3x – 5y = 7
Solution:
The given system of equations can be written as
\(\begin{bmatrix} 4 & -3 \\ 3 & -5 \end{bmatrix}\left[ \begin{matrix} x \\ y \end{matrix} \right] =\left[ \begin{matrix} 3 \\ 7 \end{matrix} \right] i.e,,AX=B\)
where \(A=\begin{bmatrix} 4 & -3 \\ 3 & -5 \end{bmatrix}\)
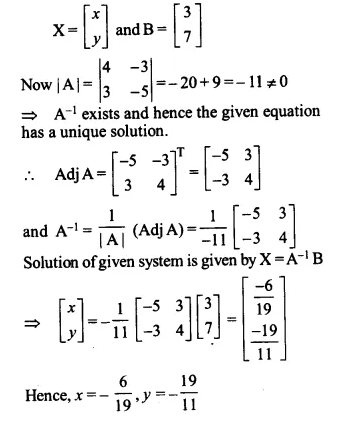
Ex 4.6 Class 12 Maths Question 10.
5x + 2y = 3
3x + 2y = 5
Solution:
The given system of equations can be written as
\(\begin{bmatrix} 5 & 2 \\ 3 & 2 \end{bmatrix}\left[ \begin{matrix} x \\ y \end{matrix} \right] =\left[ \begin{matrix} 3 \\ 5 \end{matrix} \right] i.e,,AX=B\)
where \(A=\begin{bmatrix} 5 & 2 \\ 3 & 2 \end{bmatrix}\)

Ex 4.6 Class 12 Maths Question 11.
2x + y + z = 1,
x – 2y – z = 3/2
3y – 5z = 9
Solution:
The given system of equations are
2x + y + z = 1,
x – 2y – z = 3/2,
3y – 5z = 9
We know AX = B => X = A-1B

Ex 4.6 Class 12 Maths Question 12.
x – y + z = 4
2x + y – 3z = 0
x + y + z = 2.
Solution:
The given system of equations can be written
\(\left[ \begin{matrix} 1 & -1 & 1 \\ 2 & 1 & -3 \\ 1 & 1 & 1 \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix} x \\ y \\ z \end{matrix} \right] =\left[ \begin{matrix} 4 \\ 0 \\ 2 \end{matrix} \right] i.e,,AX=B\)

Ex 4.6 Class 12 Maths Question 13.
2x + 3y + 3z = 5
x – 2y + z = – 4
3x – y – 2z = 3
Solution:
The given system of equations can be written as:
\(\left[ \begin{matrix} 2 & 3 & 3 \\ 1 & -2 & 1 \\ 3 & -1 & -2 \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix} x \\ y \\ z \end{matrix} \right] =\left[ \begin{matrix} 5 \\ -4 \\ 3 \end{matrix} \right] i.e,,AX=B \)


Ex 4.6 Class 12 Maths Question 14.
x – y + 2z = 7
3x + 4y – 5z = – 5
2x – y + 3z = 12.
Solution:
The given system of equations can be written
\(\left[ \begin{matrix} 1 & -1 & 2 \\ 3 & 4 & -5 \\ 2 & -1 & 3 \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix} x \\ y \\ z \end{matrix} \right] =\left[ \begin{matrix} 7 \\ -5 \\ 12 \end{matrix} \right] i.e,,AX=B \)


Ex 4.6 Class 12 Maths Question 15.
If A = \(\left[ \begin{matrix} 2 & -3 & 5 \\ 3 & 2 & -4 \\ 1 & 1 & -2 \end{matrix} \right] \) Find A-1. Using A-1. Solve the following system of linear equations 2x – 3y + 5z = 11,3x + 2y – 4z = – 5, x + y – 2z = – 3
Solution:
We have AX = B
where \(A=\left[ \begin{matrix} 2 & -3 & 5 \\ 3 & 2 & -4 \\ 1 & 1 & -2 \end{matrix} \right] ,X=\left[ \begin{matrix} x \\ y \\ z \end{matrix} \right] \)


Ex 4.6 Class 12 Maths Question 16.
The cost of 4 kg onion, 3 kg wheat and 2 kg rice is Rs. 69. The cost of 2 kg onion, 4 kg wheat and 6 kg rice is Rs. 90. The cost of 6 kg onion, 2 kg wheat and 3 kg rice is Rs. 70. Find the cost of each item per kg by matrix method
Solution:
Let cost of 1 kg onion = Rs x
and cost of 1 kg wheat = Rs y
and cost of 1 kg rice = Rs z
4x+3y+2z=60
2x+4y+6z=90
6x+2y+3z=70


We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths Chapter 4 Determinants Ex 4.6 help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths Chapter 4 Determinants Ex 4.6, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.