NEET Chemistry Notes p-Block Elements – Group-17 Elements Halogens
Group-17 Elements Halogens
Group-17 Elements Halogens
Group 17 members are fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I) and astatine (At). Astatine is a radioactive element. The halogens are highly reactive non-metallic elements. Fluorine is most electronegative atom and strong oxidising agent.
Important Properties
General Configuration and Oxidation State

Ground state and excited state in fluorine will be same due to the absence of d-orbitals and oxidation state of fluorine is always -1. All the halogens are highly reactive. Halogens are strong oxidising agent and their oxidising power decreases down the group
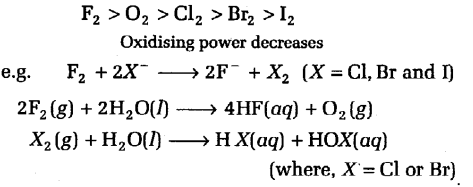
The reaction of I2with water is non-spontaneous. However, I can be oxidised by oxygen in acidic medium.
![]()
- Bond Dissociation Enthalpy
The Order of bond dissociation enthalpy is
![]()
• Fluorine shows anomalous behaviour because of its very small size and high electronegativity. F2 has less bond enthalpy than Cl2 and Br2 and the absence of d-orbitals in valence shell.
Chlorine (Cl 2)
Preparation

Chlorine is obtained by the electrolysis of brine (concentrated NaCl solution). Chlorine is liberated at anode (electrolytic process). It is also obtained as a byproduct in many chemical industries.
Properties
It is a greenish yellow gas with pungent and suffocating odour. It is soluble in water.

Some Important Compounds of Halogen
- Hydrogen chloride HCl
- Interhalogen compounds
- Oxoacids of halogen
- Oxides
Hydrogen Chloride (HCl)
- In laboratory, it is prepared by heating sodium chloride with concentrated sulphuric acid.

- HCl gas can be dried by passing through concentrated sulphuric acid.
- It is a colourless and pungent smelling gas. Its aqueous solution is called hydrochloric acid.
- When three parts of concentrated HCl and one part of concentrated HN03 are mixed, aqua-regia is formed which is used for dissolving noble metals, e.g. gold, platinum.
Interhalogen Compounds
- When two different halogens react with each other, interhalogen compounds are formed.
These compounds are covalent and diamagnetic in nature. They are volatile solids or liquids except ClF which is a gas at 298 K. Interhalogen compounds are more reactive than halogens (except fluorine). - The XY3 type compounds have bent T shape, XY5 type compounds have square pyramidal shape and IF7 has pentagonal bipyramidal structure.
Oxoacids of Halogens
Higher oxoacids of fluorine such as HF02,HF03 do not exist because fluorine is most electronegative and has the absence of d-orbitals. +3 oxidation state of bromine and iodine are unstable due to inert pair effect, therefore HBrO2 and HI02 do not exist.
Decreasing order of acidic nature

Structures of Oxoacids of Chlorine

Pseudo halide ions are stronger ligands than halide ions and these can function as ambidentate ligands as they are made up of two hetero atoms.
Oxides
- Fluorine forms two oxides, OF2 and 02F2, but only OF2 is thermally stable at 298 K. 02F2 oxidises plutonium to PuF6 and the reaction is used for removing plutonium as PuF6 from spent nuclear fuel.
- Chlorine forms a number of oxides such as, Cl20, Cl203, Cl2Og, Cl207, Cl02. Cl02 is used as a bleaching agent for paper pulp, textiles and in water treatment.
- Br20, Br02, Br03 are the least stable bromine oxides and exist only at low temperatures. They are very powerful oxidising agents.
- The iodine oxides, i.e.I204, I205,1207 are insoluble solids and decompose on heating. I205 is a very good oxidising agent and is used in the estimation of carbon monoxide.