Contents
NEET Physics Chapter Wise Mock Test – Electromagnetic Waves
Question 1:
The speed of electromagnetic waves in a vacuum, is given by
![]()
Question 2:
An electric field E and magnetic field B exist in a region. If these fields are not perpendicular to each other, then the electromagnetic wave
(a) will not pass through the region
(b) will pass through the region
(c) may pass through the region
(d) Nothing is definite
Question 3:
A radio can tune into any station in the 7.5 MHz to 12 MHz band. The corresponding wavelength band is
(a) 5 m to 15 m
(b) 2 m to 16 m
(c) 25 m to 40 m
(d) 30 m to 45 m
Question 4:
If a source is transmitting electromagnetic wave of frequency 8.2 x 106 Hz, then wavelength of electromagnetic waves transmitting from the source will be
(a) 36.6 m
(b) 40.5 m
(c) 42.3 m
(d) 50.9 m
Question 5:
A linearly polarised electromagnetic wave given as E = E0icos(kz-ωt) is incident normally on a perfectly reflecting infinite wall at z = a. Assuming that the material of the wall is optically inactive, the reflected wave will be given as
(a) Er =-E0icos(kz -ωt)
(b) Er =E0icos(kz+ωt)
(c) Er =-E0icos(kz+ωt)
(d) Er =E0isin(kz-ωt)
Question 6:
An electric charge oscillating with a frequency of 1 kilo cycle/s can radiate electromagnetic wave of wavelength
(a) 100 km
(b) 200 km
(c) 300 km
(d) 400 km
Question 7:
An electromagnetic wave going through vacuum is described by E = E0 sin(kx-ωt). Which of the following is independent of wavelength?
(a) k
(b) ω
(c) k/ω
(d) kω
Question 8:
Light with an energy flux of 18 W/cm2 falls on a non-reflecting surface at normal incidence. If the surface has an area of 20 cm2, the average force exerted on the surface during a span 30 minutes
(a) 1.2x 10-6 N
(b) 10-3 N
(c) 4x 10-7 N
(d) 5x 10-4 N
Question 9:
A large parallel plate capacitor, whose plates have an area of 1 m2 and are separated from each other by 1 mm, is being charged at a rate of 25Vs-1. If the dielectric between the plates has the dielectric constant 10, then the displacement current at this instant, is
(a) 25 μA
(b) 11 μA
(c) 2.2 μA
(d) 1.1 μA
Question 10:

Question 11:
In an electromagnetic wave, the electric and magnetic fields are 100 Vm-1 and 0.265 Am-1. The maximum energy flow is
(a) 26.5 Wm-2
(b) 36.5 Wm-2
(c) 46.7 Wm-2
(d) 765 Wm-2
Question 12:
In a plane, electromagnetic wave the electric field oscillates sinusoidally at a frequency of 2×1010 Hz and amplitude.48 Vm-1. Then, which one of the following statement is true?
(a) Wavelength of the wave is 2 x 105 m
(b) Amplitude of oscillating magnetic field is 48 T
(c) Average energy density of electric field equals the average energy density of magnetic field
(d) None of the above
Question 13:
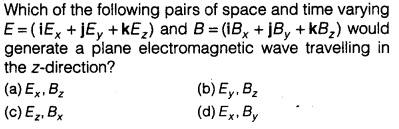
Question 14:
Consider the following two statements, regarding a linearly polarised plane electromagnetic wave.
I. Electric field and the magnetic field have equal average values.
II. Electric energy and the magnetic energy have equal average values.
(a) I is true
(b) II is true
(c) Both statements are true
(d) Both statements are false
Question 15:
In an apparatus, the electric field was found to oscillate with an amplitude of 18 Vm-1. The magnitude of the oscillating magnetic field will be
(a) 4×10-6 T
(b) 6×10-8 T
(c) 9 x 10-9 T
(d) 11 x 10-11 T
Question 16:
An electromagnetic wave going through vacuum is described by E = E0 sin(kx-ωt); B = B0 sin(kx-ωt). Which of the following equations is true ?
(a) E0k = B0ω
(b) E0ω = B0k
(c) E0B0 = ωk
(d) None of these
Question 17:
In a region of free space the electric field at some instant of time is, E= 80i + 32j – 64k and the magnetic field B = (0.2 i + 0.08j + 0.29 k). The poynting vector for these fields
(a) 11.52i-28.8j
(b) i-j
(c) 5i + 22j
(d) 2i – 18j
Question 18:
The wave of wavelength 5900A emitted by any atom or molecule must have some finite total length which is known as the coherence length. For sodium light, this length is 2.4 cm. The number of oscillations in this length will be
(a) 4.068 x 108
(b) 4.068 x104
(c) 4.068x 106
(d) 4.068x 105
Question 19:
On required 11eV of energy to dissociate a carbon monoxide molecule into carbon and oxygen atoms. The minimum frequency of the appropriate electromagnetic radiation to achieve the dissociation lies in
(a) visible region
(b) infrared region
(c) ultraviolet region
(d) microwave region
Question 20:
Electromagnetic waves are transverse in nature, is evident by
(a) polarisation
(b) interference
(c) reflection
(d) diffraction
Question 21:
21cm radiowave emitted by hydrogen in intersteller space is due to the interaction called the hyperfine interaction, is atomic hydrogen, the energy of the emitted wave is nearly
(a) 10-17 J
(b) 1J
(c) 7×10-8 J
(d) 10-24 J
Direction (Q. Nos. 22-25): In each of the following questions a statement of Assertion is given followed by a corresponding statement of Reason just below it. Of the statements mark the correct answer as
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but the Reason is not correct explanation of the Assertion
(c) If Assertion is true but Reason is false
(d) If both Assertion and Reason are false
Question 22:
Assertion (A): Electromagnetic waves exert radiation pressure.
Reason (R): Electromagnetic waves carry energy.
Question 23:
Assertion (A): For cooking in a microwave oven, food is always kept in metal containers.
Reason (R): The energy of microwave is easily transferred to the food in metal container
Question 24:
Assertion (A): X-ray astronomy is possible only from satellites orbiting the earth.
Reason (R): Efficiency of X-rays telescope is large as compared to any other telescope.
Question 25:
Assertion (A): Microwave propagation is better than the sky wave propagation.
Reason (R): Microwaves have frequencies 100 to 300 GHz, which have very good directional properties.
Question 26:
Which of the following statement is false for the properties of electromagnetic waves ?
(a) Both electric and magnetic field vectors attain the maxima and minima at the same place and same time
(b) The energy in electromagnetic wave is divided equally between electric and magnetic vectors
(c) Both electric and magnetic field vectors are parallel to each other and perpendicular to the direction of propagation of wave
(d) These waves tlo not require any material medium for propagation
Question 27:
The ratio of amplitude of magnetic field to the amplitude of electric field for an electromagnetic wave propagating in vacuum is equal to
(a) the speed of light in vacuum
(b) reciprocal of speed of light in vacuum
(c) the ratio of magnetic permeability to the electric susceptibility of vacuum
(d) unity
Question 28:
The electric field associated with an electro magnetic wave in vacuum, is given by E = i 40 cos(kz-6×108t), where E, z and t are in Volt/m, metre and second, respectively. The value of wave vector k is
(a) 2 m-1
(b) 0.5 m-1
(c) 6 m-1
(d) 3 m-1
Question 29:
The electric and the magnetic field, associated with an electromagnetic wave, propagating along the +Z-axis, can be represented by
(a) E=E0k,B=B0i
(b) E=E0j,B=B0j
(c) E=E0 j,E=B0k
(d) E=E0i,B=B0j
Question 30:
A uniform electric field and an uniform magnetic field are acting along the same direction in a certain region. If an electron is projected in the region, such that its velocity is pointed along the direction of fields, then the electron
(a) speed will decrease
(b) speed will increase
(c) will turn towards left of direction of motion
(d) will turn towards right of direction of motion
Answers:

Hints And Solutions:





