NEET Physics Notes Waves-Sound Waves
Sound Waves
Sound Waves
Mechanical waves in air having a frequency ranging from 20 Hz to 20 kHz are known as audio waves or sound waves. Waves having frequencies less than 20 Hz are known as the infrasonic waves. Waves in air having frequencies greater than 20 kHz are known as ultrasonic waves.
- Velocity of sound in air = 332 ms-1
- Velocity of sound in water = 1400 ms-1
- Velocity of sound in steel =5000 ms-1
Sound exhibits reflection, refraction, interference and diffraction but not polarisation.
Relation between Phase Difference, Path Difference and Time Difference

Displacement Relation for a Progressive or Harmonic Wave
The equation of a plane progressive or simple harmonic wave travelling along positive direction of x-axis is

If maximum value of y = a i.e. a is maximum amplitude, then

Principle of Superposition ofWaves
When two or more than two waves of similar type propagate in a medium simultaneously, then resultant displacement of any particle of the medium is equal to the vector sum of displacements produced by individual waves separately. This principle is called principle of superposition of waves
y=y 1+y 2+y 3+……..
Interference ofWaves

When two waves of same frequency (or same wavelength) travelling along same path superimpose each other, there occurs redistribution of energy in the medium. If at a given position (x being constant) displacement due to two waves be
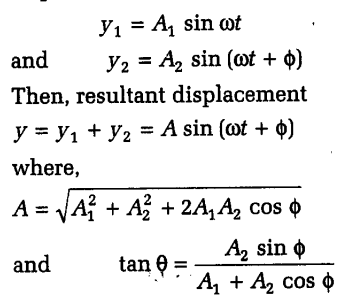

This is known as constructive interference.

Reflection and Transmission of Waves
When sound waves are incident on a boundary separating two media, a part of it is reflected back into the initial medium while the remaining is partly absorbed and partly transmitted into the second medium.